https://qillknows.wordpress.com/
QMRA is taking a part in Risk Assessment part. Here, there are 4 steps need to be taken into account, Hazard identification, Hazard Characterization, Exposure assessment, and Risk Characterization. The process starts with hazard identification and hazard characteristic, where the type of micro-bacteria (Salmonella, Listeria, E. Coli, etc) is introduced. In addition, the characteristic of determined micro-bacteria need to be studied to better understand how the micro-bacteria is grow and in what circumstances.
The next step is exposure assessment. Exposure assessment is defined as an assessment to measure how likely it is that an individual or a population will be exposed to a microbial hazard and what numbers of organisms are likely to be ingested [1]. In this step, the lineage of food distribution is drawn and each process involved is described to see the transmission of hazard. Each process involved in food pathway is assigned with basic process to measure prevalence and concentration of microbaterial occurs in each process. The measurement take into account variability and uncertainty in microbacterial transmission.
There are 6 basic processes in exposure assessment that can affect the transmission of microbacterial. They are Growth, Inactivation, Partitioning, Mixing, Removal, and Cross Contamination. Growth and inactivation are 2 basic microbial processes, which are strongly depends on the characteristic of micro-bacterial investigated and the environmental condition surrounds it. Meanwhile, partitioning, mixing, removal, and cross contamination are 4 handling process which are determined by how the food is handled assuming a uniform distribution of micro-organism over the food matrix. Figure 10 shows the schematic representation of exposure assessment. Figure below shows the schematic representation of exposure assessment.
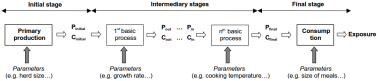
The last step is risk characterization where we combine all the outcome of the hazard characterization and exposure assessment in order to see the likelihood and severity caused by investigated hazard. Risk characterization is aiming to create a model of a person that is exposed with enough pathogen to catch the disease in population. Therefore, the conclusion of risk characteristic is more valid in population rather than in a single person.
references:
[1] A. M. Lammerding and A. Fazil, “Hazard identification and exposure assessment for microbial food safety risk assessment,” International Journal of Food Microbiology, 2000.